Introduction
Alzheimer’s and dementia are progressive cognitive disorders that pose significant challenges for individuals and their families. While there is currently no cure, there are proactive measures individuals can take to reduce the risk of developing these conditions. This article explores various lifestyle choices and strategies that can contribute to maintaining cognitive health and potentially lowering the risk of Alzheimer’s and dementia.
Understanding Alzheimer’s and Dementia
Alzheimer’s disease and dementia are neurodegenerative disorders characterized by cognitive decline, memory loss, and impaired daily functioning. These conditions often impact the quality of life of affected individuals and present emotional and practical challenges for their families.
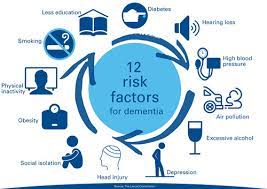
Risk Factors for Alzheimer’s and Dementia
Both genetic and lifestyle factors contribute to the risk of developing Alzheimer’s and dementia. While some risk factors, such as age and genetics, are beyond control, lifestyle choices can play a significant role in reducing overall risk.
The Role of Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can have a positive impact on cognitive health. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical exercise, staying mentally active, and managing stress.
Regular Physical Exercise
Physical activity has been linked to a lower risk of cognitive decline. Regular exercise promotes healthy blood flow to the brain, reduces inflammation, and enhances overall brain function. Activities such as walking, swimming, or even gardening can contribute to cognitive well-being.
A Balanced and Brain-Boosting Diet
Certain foods are known to support brain health and may help reduce the risk of cognitive decline. These include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Adopting a Mediterranean-style diet has been associated with a lower risk of Alzheimer’s.
Cognitive Stimulation and Mental Activities
Engaging in mentally stimulating activities helps keep the brain active and may contribute to cognitive resilience. Reading, solving puzzles, learning a new skill, or participating in activities that challenge the mind are all beneficial for cognitive health.
Quality Sleep and Its Cognitive Benefits
Adequate sleep is essential for cognitive function and memory consolidation. Poor sleep patterns and disorders have been linked to an increased risk of cognitive decline. Establishing good sleep hygiene practices can positively impact cognitive well-being.
Social Connections and Their Impact
Maintaining strong social connections is crucial for cognitive health. Regular social interactions and meaningful relationships have been associated with a reduced risk of cognitive decline. Activities that foster social engagement, such as joining clubs or volunteering, contribute to overall well-being.
Managing Chronic Conditions
Conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and obesity can increase the risk of cognitive decline. Managing these conditions through lifestyle changes, medication, and regular medical check-ups can contribute to cognitive health.
Reducing Stress for Cognitive Well-being
Chronic stress has been linked to cognitive impairment. Adopting stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, yoga, or meditation, can positively impact both mental and physical health.
Regular Health Check-ups and Cognitive Assessments
Regular health check-ups can help identify and manage risk factors early on. Cognitive assessments, especially in older age, can contribute to the early detection of cognitive decline, allowing for timely intervention.
Staying Mentally Active in Older Age
As individuals age, staying mentally active becomes even more crucial. Engaging in activities that challenge the mind, such as learning a new language or playing musical instruments, can contribute to cognitive vitality.
Alcohol and Tobacco Moderation
Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking have been associated with cognitive decline. Moderation or cessation of these habits can contribute to overall health, including cognitive well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while there is no guaranteed method to prevent Alzheimer’s and dementia, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk and contribute to overall cognitive well-being. From regular physical exercise to maintaining a balanced diet, staying socially connected, and managing stress, individuals have the power to positively impact their cognitive health and potentially lower the risk of developing these challenging conditions. Taking proactive steps towards a healthy lifestyle is an investment in long-term cognitive resilience.
FAQs
Can adopting a healthy lifestyle really reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s and dementia?
Yes, research suggests that adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and mental stimulation, can contribute to a lower risk of Alzheimer’s and dementia.
Is there a specific age to start implementing these lifestyle changes?
It’s never too early or too late to adopt a healthy lifestyle. However, incorporating these habits earlier in life may have a more significant impact on long-term cognitive health.
How often should cognitive assessments be done?
The frequency of cognitive assessments may vary based on individual health factors. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers can help determine the appropriate timing for cognitive assessments.
Do genetics play a significant role in the risk of Alzheimer’s?
While genetics can contribute to the risk, lifestyle choices and environmental factors also play a crucial role. Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate the impact of genetic factors.
Are there specific mental activities recommended for older adults?
Activities such as reading, puzzles, learning new skills, and engaging in social interactions are beneficial for older adults to stay mentally active and support cognitive health.