Introduction
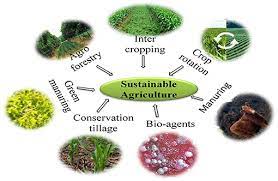
Sustainability in agriculture is a crucial aspect that revolves around employing practices that meet current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own. As our planet faces environmental challenges, the sustainable agriculture and farming industry emerges as a beacon of hope. This article explores the key principles, techniques, benefits, challenges, and the promising future of sustainable agriculture.
Key Principles of Sustainable Agriculture
Soil Health and Conservation
Sustainable farming begins with nurturing the very foundation—soil. Practices such as cover cropping, crop rotation, and minimal tillage enhance soil health and reduce erosion.
Water Management
Efficient water usage is paramount in sustainable agriculture. Drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and smart irrigation systems help conserve water resources.
Biodiversity Preservation
Maintaining a diverse ecosystem on the farm promotes natural pest control and pollination. This can be achieved through hedgerows, buffer zones, and the integration of native plants.
Integrated Pest Management
Sustainable farms prioritize biological control methods, crop rotation, and the use of natural predators to manage pests, minimizing reliance on chemical solutions.
Sustainable Farming Techniques
Organic Farming
Eliminating synthetic inputs, organic farming relies on natural processes to maintain soil fertility and control pests, resulting in healthier produce.
Agroforestry
Integrating trees into farming systems offers benefits such as improved soil structure, enhanced biodiversity, and additional income through timber or fruit production.
Precision Farming
Leveraging technology, precision farming optimizes inputs like water and fertilizers, reducing waste and environmental impact while increasing efficiency.
Benefits of Sustainable Agriculture
Environmental Impact
Sustainable practices contribute to soil and water conservation, reduced pollution, and the preservation of biodiversity, fostering a healthier planet.
Economic Sustainability
Despite initial investment costs, sustainable farming proves economically viable through improved soil quality, reduced input costs, and increased market demand for eco-friendly products.
Social and Community Benefits
Sustainable agriculture fosters community engagement, supports local economies, and ensures equitable distribution of resources, contributing to social well-being.
Challenges in Implementing Sustainable Practices
Initial Costs
Adopting sustainable practices may require upfront investments, posing challenges for small-scale farmers. However, long-term benefits often outweigh these initial expenses.
Education and Awareness
Many farmers may lack knowledge about sustainable practices. Education and awareness programs are essential to bridge this gap and promote widespread adoption.
Policy and Regulations
Governments need to create supportive policies and regulations to encourage and reward sustainable farming practices, creating an enabling environment for farmers.
Success Stories in Sustainable Agriculture
Case Study 1: [Farm Name]
Highlighting a farm that successfully transitioned to sustainable practices, showcasing increased yields and positive environmental impact.
Case Study 2: [Farm Name]
Exploring another farm’s journey towards sustainability, emphasizing the economic and social benefits achieved.
The Future of Sustainable Agriculture
Technological Advancements
Innovations like precision agriculture, drone technology, and genetic engineering hold promise for further optimizing sustainable farming practices.
Global Initiatives
International efforts and agreements aim to promote sustainable agriculture globally, emphasizing collaboration and shared responsibility for a sustainable future.
Conclusion
In the quest for a greener and more sustainable future, the agriculture and farming industry plays a pivotal role. Embracing sustainable practices benefits not only the environment but also farmers and communities at large. As we move forward, it is essential to continue supporting and adopting these practices for the well-being of our planet and future generations.
FAQs
- Q: How can small-scale farmers afford the initial costs of sustainable practices? A: There are various government and NGO programs that provide financial assistance and support for small-scale farmers transitioning to sustainable practices.
- Q: What role does technology play in sustainable agriculture? A: Technology, such as precision farming and innovative irrigation systems, enhances efficiency, reduces waste, and contributes to the overall sustainability of farming practices.
- Q: Are there any downsides to organic farming? A: While organic farming has numerous benefits, challenges include lower yields and potential difficulty in meeting high market demand.
- Q: How can consumers contribute to sustainable agriculture? A: By choosing sustainably sourced and produced products, consumers can create demand for eco-friendly farming practices, encouraging more farmers to adopt sustainability.
- Q: What can governments do to promote sustainable agriculture? A: Governments can enact policies that incentivize and reward sustainable practices, invest in education and awareness programs, and collaborate on international initiatives for a global impact.