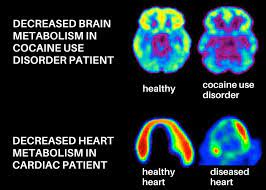
Addiction is a complex and challenging condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Understanding the science behind addiction is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and supporting individuals on their journey to recovery. In this article, we will explore the science of addiction, shedding light on its neurological and psychological aspects, and discuss pathways to recovery.
- Introduction
Addiction is a chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking, continued use despite harmful consequences, and long-lasting changes in the brain. It impacts not only the individual but also their relationships, work, and overall well-being.
- The Neurobiology of Addiction
At its core, addiction involves changes in the brain’s structure and function. The brain’s reward system, primarily the release of neurotransmitter dopamine, plays a central role. Substance use triggers an excessive release of dopamine, creating a euphoric sensation. Over time, the brain adapts to this flood of dopamine, reducing its sensitivity and requiring more substance use to achieve the same pleasure.
- The Role of Dopamine
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. In addiction, substances or behaviors that trigger dopamine release become associated with pleasure, creating a powerful incentive to repeat the behavior. This process contributes to the development of cravings and compulsive drug-seeking behavior.
- Brain Changes and Cravings
Long-term substance use leads to structural and functional changes in the brain. The prefrontal cortex, responsible for decision-making and impulse control, becomes impaired. Simultaneously, the amygdala, associated with emotional responses, becomes hyperactive, intensifying cravings and impulsive behavior.
- Genetics and Vulnerability
Genetics can contribute to an individual’s vulnerability to addiction. Certain genes may influence how the brain responds to substances, affecting the likelihood of developing an addiction. However, genetics alone do not determine addiction; environmental factors and personal choices also play significant roles.
- The Psychology of Addiction
Beyond neurological changes, addiction has psychological components. Trauma, stress, mental health disorders, and environmental factors can contribute to the development and perpetuation of addictive behaviors. Understanding these underlying issues is crucial for comprehensive addiction treatment.
- Dual Diagnosis: Addressing Co-occurring Disorders
Many individuals struggling with addiction also have co-occurring mental health disorders. This is known as a dual diagnosis. Effective treatment involves addressing both the addiction and any underlying mental health issues simultaneously for holistic recovery.
- Stages of Change Model
Recovery from addiction often follows the Stages of Change Model, which includes precontemplation, contemplation, preparation, action, maintenance, and relapse prevention. Recognizing where individuals are in this process helps tailor interventions to their specific needs.
- Treatment Approaches
Various treatment approaches exist for addiction, ranging from behavioral therapies and counseling to pharmacological interventions. Behavioral therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and motivational enhancement therapy (MET), aim to modify patterns of thinking and behavior associated with substance use.
- Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT)
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT) involves the use of medications, along with counseling and behavioral therapies, to address substance use disorders. MAT is particularly effective for opioid and alcohol use disorders, helping manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings.
- Support Groups and Peer Recovery
Support groups, such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) and Narcotics Anonymous (NA), play a crucial role in recovery. Peer support provides individuals with a sense of community, shared experiences, and accountability, contributing to long-term success.
- Holistic Approaches to Recovery
Holistic approaches to recovery consider the whole person—body, mind, and spirit. Incorporating activities such as yoga, meditation, exercise, and nutritional therapy promotes overall well-being and complements traditional addiction treatment.
- Relapse and Relapse Prevention
Relapse is a common part of the recovery process. Understanding its triggers and developing relapse prevention strategies are essential. Learning from relapses helps individuals strengthen their coping skills and resilience.
- The Importance of Aftercare
Aftercare is crucial for sustained recovery. Continuing support through outpatient counseling, support groups, and ongoing mental health care helps individuals navigate the challenges of daily life without resorting to substance use.
- Breaking the Stigma
Breaking the stigma surrounding addiction is vital for fostering empathy and support. Recognizing addiction as a medical condition rather than a moral failing promotes understanding and encourages individuals to seek help without fear of judgment.
Conclusion
Understanding the science of addiction is the foundation for developing effective treatment strategies and supporting individuals on their journey to recovery. By addressing both the neurological and psychological aspects of addiction and embracing a holistic approach, we can empower individuals to overcome the challenges of addiction and build a healthier, fulfilling life.
FAQs
Is addiction solely a result of poor choices?
- No, addiction involves complex interactions between genetics, neurological changes, and environmental factors. It is not solely a result of poor choices, and individuals struggling with addiction deserve empathy and support.
Can addiction be cured?
- Addiction is considered a chronic condition, and while it can be effectively managed, there is no definitive cure. Recovery is an ongoing process that requires ongoing support and self-care.
Are there age-specific considerations in addiction treatment?
- Yes, age can influence the approach to addiction treatment. Treatment plans may need to consider developmental stages, family dynamics, and unique challenges associated with different age groups.
What role do family and friends play in the recovery process?
- Family and friends play a crucial role in providing support during the recovery process. Their understanding, encouragement, and involvement in the treatment plan contribute to an individual’s overall success.
How can employers support employees in addiction recovery?
- Employers can support employees in recovery by fostering a supportive workplace culture, providing resources for treatment, and offering flexibility to accommodate recovery-related needs.