1. Introduction
Defining Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS)
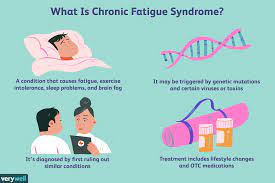
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS), also known as Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (ME), is a complex and debilitating condition characterized by persistent and unexplained fatigue that significantly impacts daily functioning.
Prevalence and Impact on Daily Life
CFS affects millions of people globally, with a notable impact on their ability to carry out routine activities. Despite its prevalence, CFS is often misunderstood, and individuals with the condition may face challenges in diagnosis and accessing appropriate care.
2. Symptoms and Diagnostic Criteria
Primary Symptoms of CFS
The hallmark symptom of CFS is profound fatigue that lasts for at least six months and is not alleviated by rest. Other common symptoms include cognitive difficulties, unrefreshing sleep, muscle pain, and post-exertional malaise (PEM).
Criteria for Diagnosing Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Diagnosing CFS involves meeting specific criteria outlined by healthcare organizations. These criteria include the presence of persistent fatigue, along with the exclusion of other medical and psychiatric conditions that may cause similar symptoms.
3. Possible Causes and Triggers
The Multifactorial Nature of CFS
The exact cause of CFS remains unknown, and research suggests a multifactorial origin involving genetic, immunological, and environmental factors. Understanding these complex interactions is crucial for developing targeted treatments.
Common Triggers and Associations
Certain triggers and associations have been identified in individuals with CFS, including viral infections, hormonal imbalances, and significant stressors. Exploring these factors can provide insights into the onset and progression of the condition.
4. Seeking Medical Help
Importance of Consulting Healthcare Professionals
If someone suspects they have CFS, seeking medical help is essential. Healthcare professionals, including primary care physicians and specialists, play a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of CFS.
Diagnostic Process and Differential Diagnosis
The diagnostic process involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and the exclusion of other medical conditions. Differential diagnosis is crucial to rule out illnesses that may mimic CFS symptoms.
5. Treatment Approaches
Individualized Treatment Plans
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to treating CFS. Individualized treatment plans consider the unique symptoms and needs of each person. Treatment may involve a combination of medications, lifestyle adjustments, and complementary therapies.
Managing Symptoms and Improving Quality of Life
While there is no cure for CFS, symptom management is a primary focus of treatment. Medications may target specific symptoms such as pain, sleep disturbances, and mood disorders. Additionally, lifestyle modifications aim to improve overall well-being.
6. Lifestyle Modifications
Balancing Activity and Rest
Finding the right balance between activity and rest is crucial for individuals with CFS. Pacing oneself and incorporating periods of rest during the day can help manage symptoms and prevent exacerbations.
Nutrition and Hydration in CFS Management
Proper nutrition and hydration are vital components of CFS management. Ensuring a well-balanced diet with adequate nutrients and staying hydrated contribute to overall health and may positively impact energy levels.
7. Coping Strategies
Dealing with Emotional and Mental Health Aspects
Living with CFS can take a toll on emotional and mental health. Coping strategies, including counseling, support groups, and mindfulness practices, can help individuals navigate the challenges associated with the condition.
Support Systems and Patient Communities
Building a strong support system is essential for those with CFS. Connecting with patient communities and support groups provides a platform for sharing experiences, advice, and emotional support.
8. Research and Advancements
Ongoing Studies and Clinical Trials
Researchers continue to explore the underlying mechanisms of CFS and potential treatment options. Ongoing studies and clinical trials contribute to advancements in understanding and managing this complex condition.
Potential Future Developments in CFS Understanding
As research progresses, there is hope for uncovering new insights into CFS, leading to more targeted treatments and improved outcomes for individuals living with the condition.
9. Addressing Common Misconceptions
Dispelling Myths Surrounding CFS
CFS is often surrounded by misconceptions, including beliefs that it is solely a psychological condition or that individuals can overcome it through sheer willpower. Dispelling these myths is essential for fostering empathy and accurate understanding.
Raising Awareness for Accurate Understanding
Educating the public and healthcare professionals about CFS is crucial for raising awareness and improving the support and resources available to individuals affected by the condition.
10. Conclusion
Living with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Living with CFS presents unique challenges, but with proper diagnosis, individualized treatment, and ongoing support, individuals can manage symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Encouragement for Those Affected
To those affected by CFS, it is essential to seek understanding, support, and access to appropriate healthcare. By advocating for oneself and staying informed, individuals with CFS can navigate the complexities of the condition with resilience and hope.
FAQs
- What are the primary symptoms of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS)?
- The primary symptoms include persistent and unexplained fatigue lasting at least six months, cognitive difficulties, unrefreshing sleep, muscle pain, and post-exertional malaise (PEM).
- How is Chronic Fatigue Syndrome diagnosed?
- Diagnosing CFS involves meeting specific criteria, including persistent fatigue and the exclusion of other medical and psychiatric conditions that may cause similar symptoms.
- What are the possible causes and triggers of CFS?
- The exact cause of CFS is unknown, but it is believed to involve genetic, immunological, and environmental factors. Triggers may include viral infections, hormonal imbalances, and significant stressors.
- Is there a cure for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome?
- Currently, there is no cure for CFS. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life through individualized plans that may include medications, lifestyle adjustments, and complementary therapies.
- How can individuals with CFS cope with the emotional and mental health aspects of the condition?
- Coping strategies such as counseling, support groups, and mindfulness practices can help individuals with CFS navigate the emotional and mental health challenges associated with the condition.